CT SCAN - Computerized Tomography Scan
Pictures of structures within the body created by a computer that takes the data from multiple X-ray images and turns them into pictures on a screen. CT stands for computerized tomography.
The CT scan can reveal some soft-tissue and other structures that cannot even be seen in conventional X-rays. Using the same dosage of radiation as that of an ordinary X-ray machine, an entire slice of the body can be made visible with about 100 times more clarity with the CT scan.
The tomograms ("cuts") for CT are usually made 5 or 10 mm apart. The CT machine rotates 180 degrees around the patient's body. The machine sends out a thin X-ray beam at 160 different points. Crystals positioned at the opposite points of the beam pick up and record the absorption rates of the varying thicknesses of tissue and bone. The data are then relayed to a computer that turns the information into a 2-dimensional cross-sectional image.
The CT scanner was invented in 1972 by the British engineer Godfrey N. Hounsfield (later Sir Godfrey) and the South African (later American) physicist Alan Cormack. CT scanning was already in general use by 1979, the year Hounsfield and Cormack were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology for its development.
The CT scan is also known as the CAT (computerized axial tomography) scan. 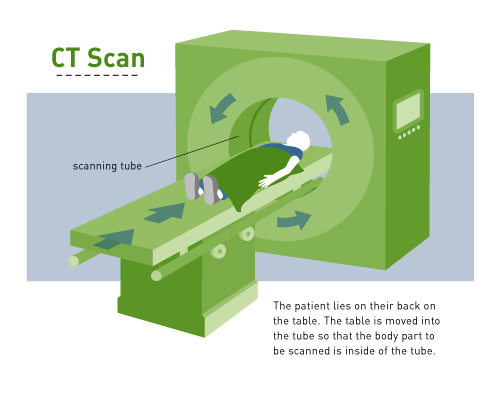
|






